As we all know, LED (Light Emitting Diode), light-emitting diode, is a solid-state semiconductor device that can directly convert electrical energy into light energy. The heart of the LED is a semiconductor chip. One end of the chip is attached to a bracket, which is the negative pole, and the other end is connected to the positive pole of the power supply. The entire chip is encapsulated by epoxy resin.
The semiconductor wafer is composed of two parts, one part is a P-type semiconductor, in which holes dominate, and the other end is an N-type semiconductor, which is mainly electrons. But when these two semiconductors are connected, a "P-N junction" is formed between them. When the current acts on the chip through the wire, electrons will be pushed to the P area, where the electrons and holes recombine, and then emit energy in the form of photons. This is the principle of LED light emission. The wavelength of light determines the color of light, which is determined by the material forming the P-N junction.
When the LED converts electrical energy into light energy, when the current flows through the LED components, the temperature of the PN junction will rise, forming the so-called luminous heating, that is, the higher the current and the higher the temperature, the higher the brightness of the light. Many people here may say, if this is the case, then why control the temperature of the LED?

To understand this problem, let's take a look at how high temperature affects LEDs and LED lamps.
The effect of temperature on LED
①LED is mainly composed of bracket, silver glue, chip, gold wire (copper wire) and epoxy resin. In addition to bracket and epoxy resin, damage to the other three materials can directly cause the LED to stop working, and the high is too high. The temperature of the above three materials is exactly the nemesis of the above three materials. In a high temperature environment, the light attenuation of the LED will increase, reducing the life of the LED, and even worse, it can even burn the gold wire (copper wire) in an instant to cause the LED Direct damage.
②Single LED can not directly meet the needs of use. Often accompanied by LEDs, there is also an LED power supply (drive). The power supply itself is a heating element, which has its own temperature resistance requirements. The disabling or even damage of the LED lamps causes the LED lamps to not work normally.
Therefore, it is imperative to solve the temperature problem of LEDs and LED lamps, that is, heat dissipation.
Principle of heat dissipation
Heat dissipation in the traditional sense is the so-called heat transfer, and the principle of heat transfer has the following three points:
1 Conduction
As everyone knows, heat can be conducted through the medium, and it can be transferred from a location where the temperature is too high to a location where the temperature is too low. In this case, the conductivity of the material, the thermal resistance caused by the structure of the radiator, and the shape and size are all May interfere with heat conduction.
2 radiation
The high school physics teacher told us that the heat goes up. In fact, this is the so-called radiation, which is very limited to the surrounding environment and the material of the radiator itself.
3 convection
People who buy a building should have heard the concept of a one-floor building. Sales generally say that such a building is very cool. It is true. The so-called convection is to dissipate heat through the flow of gas or liquid, and its heat dissipation rate generally depends on the flow. Speed, if you want to achieve on the lamp body is difficult (considering factors such as waterproof, safety, etc.), but it is not without specific reference to the product shown below.
The heat dissipation of the above three points, and now the most used in lamps and lanterns is heat conduction, which is also the topic we focus on today.
Heat Conduction
Therefore, there are three factors that affect heat conduction: material, structure, and size.
1 material
The material composition of LED lamps: First of all, one of the most common LED lamps is composed of heat sink (lamp body), LED, substrate, power supply driver, and optical components. Among them, the heating element has two LEDs and two drivers, and the heat sink has a heat sink, a substrate, or an optical element made of aluminum (the amount of heat conduction is almost negligible).

heat sink
The radiators of LED lamps are generally made of aluminum, which can be divided into two categories, stretched aluminum mainly made of aluminum such as AL6060, and die-cast aluminum mainly made of ADC12. Among them, the thermal conductivity of ADC12 is 96.7w/m ℃, and aluminum materials such as AL6060 are 198~250w/m ℃. The latter is better than the former in terms of thermal conductivity. Someone may ask here, since aluminum materials such as AL6060 The heat conduction is so good, why is there still ADC12 appearing?
① ADC12 die-cast aluminum, it is mass-produced quickly, and can meet the general requirements of design aesthetics (almost the shape you can think of can be presented), but because it can be modified low, the cost of designing molds is high, and it is generally used when the size is not very large. For products that do not need to be modified, it is also relatively cheap, so it has occupied the shell market for a long time.
② Stretched aluminum has strong thermal conductivity, and the mold cost is generally one-tenth that of die-casting molds. The length change is also very flexible, and the processing and mass production are fast. However, the reasons why it cannot fully occupy the shell market are as follows: insufficient hardness, It is easy to deform, and the appearance can only be stretched, with few changes, which cannot meet the market appearance requirements.
Based on the above two points, it can be concluded that heat-dissipating stretched aluminum is better than die-cast aluminum, and the appearance of the latter is better than the former, depending on the cost requirements and appearance requirements of the design.
Substrate
In addition to the housing, the substrate is also one of the important heat sinks. Commonly used heat dissipation substrates for LED lamps on the market include copper substrates and aluminum substrates. Among them, the thermal conductivity of copper substrates is better than that of aluminum substrates, but the price is relatively high. , A large part of designers or companies will choose aluminum substrate as a heat sink.
structure
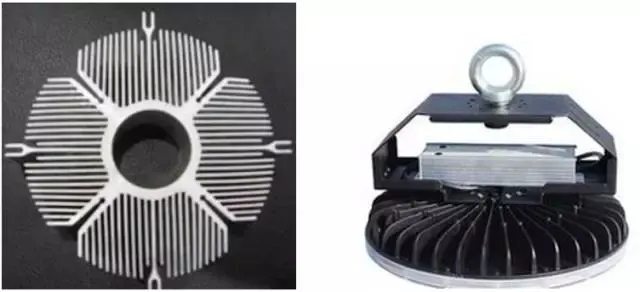
①The fin design in the following figure can be adopted in appearance。
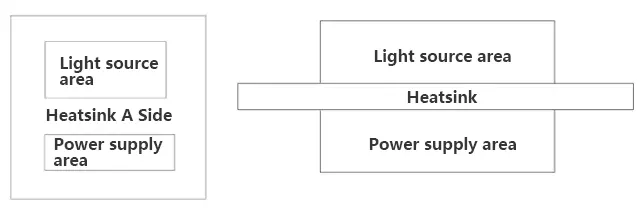
②At the initial stage of design, the placement of electronic components should be well thought out to avoid common heat sources in the following illustrations.
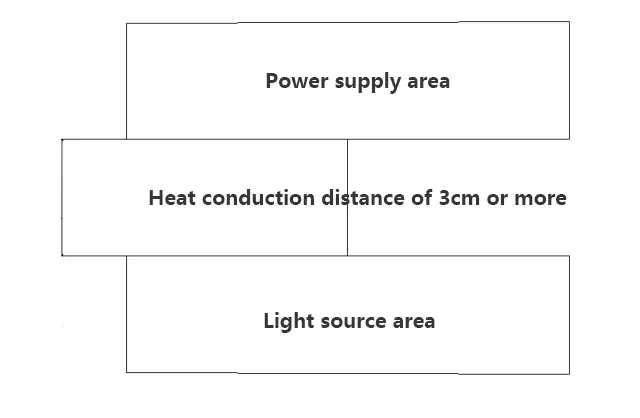
③With the permission of the structure, it is best not to fix the position of the power supply under the light source, because according to the principle of heat circulation, the heat goes upwards. If there is really no way to control it, it is best to reserve the conduction distance to 3CM or more (as for why, please Baidu heat conduction related knowledge). The design plan is shown in the figure below.
3 Size
For example, a square meter of material can derive 1W of heat, and a square meter of material can derive 100W of heat. The concept is very clear. There is no need to elaborate. The only recommendation here is to choose a reasonable size within a reasonable range.
Misunderstanding of heat dissipation
From the above information, it can be understood that thermal conductivity is very important for the heat dissipation of lamps, so many people will choose better heat dissipation materials, so they are superstitious about the so-called high-tech materials that are high in price and have not been verified by many parties. In fact, Experiments have shown that using ordinary aluminum to dissipate heat, after many tests, the temperature of the heat sink is only 3-5° higher than some so-called high-tech heat dissipation materials. A good material can only reduce the temperature by 3-5° when the thermal resistance is zero, but the cost is another matter.
In addition to materials, there are also big misunderstandings on heat pipes. First, let’s talk about what a heat pipe is. A heat pipe (called a heat pipe) is a special material with fast uniform temperature characteristics. The hollow metal tube body makes it light in weight. The characteristics of heat pipes, and its fast uniform temperature characteristics, make it have excellent thermal superconductivity; the application range of heat pipes is quite wide, the earliest used in the aerospace field, and now it has been widely used in various heat exchangers, coolers, Natural geothermal references, etc., play the role of rapid heat conduction, and it is the most common and efficient heat conduction (non-heat dissipation) element in the current electronic product heat dissipation device.
The heat derived from the heat sink eventually needs to be transported away by air convection. If there is no support from the heat sink fins, the heat pipe will quickly reach thermal equilibrium, and the temperature rises together with the heat sink, which is of little significance. If fins are added, fins will eventually be used to dissipate heat, and the contact points between the fins and the heat pipe are not as good as other methods, which will also increase the cost and the heat dissipation effect will not be improved. Therefore, when using heat pipes, try to consider the rationality of its structure and not blindly use it.
There are three heat dissipation points: conduction, convection, and radiation. I have already explained conduction and convection. Next, let’s talk about radiation. In fact, it doesn’t make much sense for the heat dissipation of lamps. However, many people will listen to what those manufacturers say about nano Radiation materials or something, in fact, this is really negligible for the lamps. why? First of all, for lamps, the temperature range is about 50-80°, and in this case, even if the radiating material reaches the radiating ability of black body radiation, it can also play a few percent of the heat dissipation, and the coating It hinders the heat conduction and affects the heat dissipation of the lamp.