

On June 3, Nokia announced in Espoo, Finland, that its 5G AirScale liquid-cooled base station solution has helped Finnish mobile operator Elisa to reduce the potential energy costs of its base stations by 30% and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by about 80%. This is the first deployment of a commercial 5G liquid-cooled base station solution in the world, demonstrating Nokia's firm commitment to sustainable development and climate change.

While reducing energy and emissions, Nokia said that liquid-cooled base stations run quietly and require no maintenance. In addition, compared with standard active air conditioning equipment, the volume is reduced by up to 50% and the weight is reduced by 30%. Liquid cooling technology saves a lot of operating costs for base station site operators and extends the service life of base station components as much as possible.
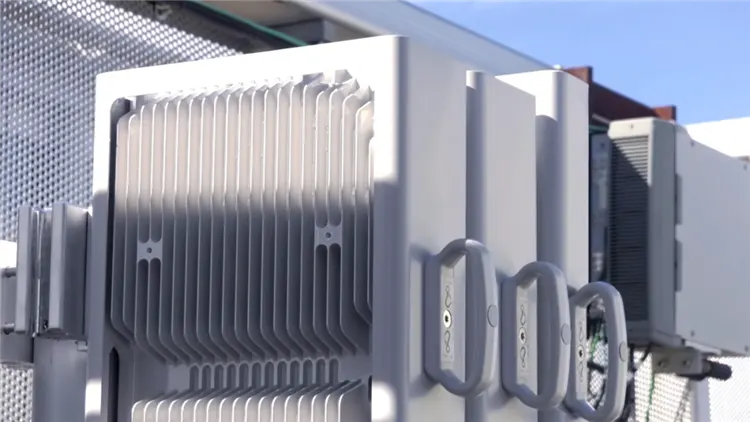

NOKIA 5G AirScale liquid-cooled base station
It is reported that Nokia announced its successful deployment of the world's first 5G liquid-cooled base station system on its official website on December 10, 2018. At MWC in 2017, Nokia once demonstrated Bell Labs liquid-cooled base station technology. With the continuous evolution of wireless technology from 2G to 5G, the power consumption of base stations is 2-3 times that of the 4G era. The traditional air-cooling system is about 4000 times smaller than water because of the heat capacity of air. Compared with the liquid cooling system, the traditional air-cooling system Energy efficiency is too low. Therefore, 5G base stations require more advanced liquid cooling systems.
Single-phase liquid-cooled coolant is driven by a pump and flows in the channel to take away heat. The most common application is water-cooled plates, which is a relatively mature technology. The cost of water-cooled plates is mainly concentrated in materials, runner forming and welding.
The picture below shows the prototype of a liquid-cooled plate designed by Toyota using COMSOL Multiphysics® software for simulation topology design.
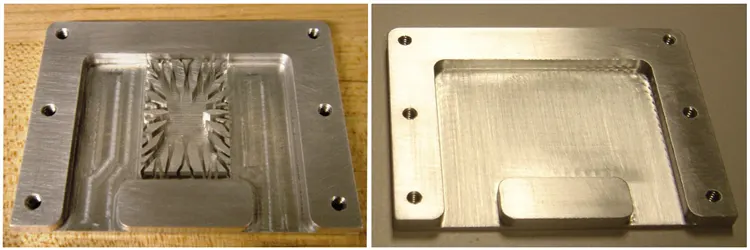
The picture on the left is a prototype of an aluminum heat sink with a layered micro-channel topology; the picture on the right is a prototype of an aluminum heat sink without a topology.
Now, we can also use AI computing technology to develop a topological design runner liquid cooling plate with a cooling efficiency increase of 20%.
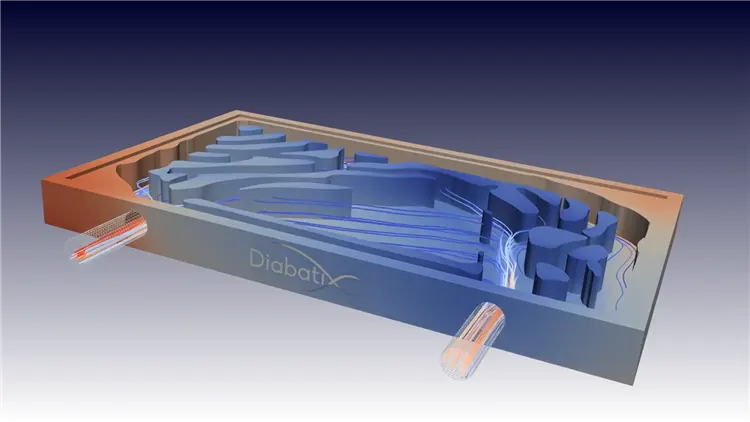
Diabatix company uses AI to drive the topological design of the flow channel of the liquid-cooled radiator. The design is optimized for uniform surface temperature. The design method automatically considers flow restrictions (flow rate, pressure drop), thermal properties of the materials used, and manufacturing restrictions (such as CNC milling). Compared with the traditional design, under the same flow conditions, an efficiency improvement of up to 20% can be achieved.
For the one-time grooving and sealing welding of the simple runner of the water-cooled plate, please refer to our other report for details: Coreflow: TWI new machining technology, or trigger a revolution in the water-cooled plate industry.
Next, we will briefly introduce the two-phase liquid cooling. Two-phase liquid cooling is an efficient cooling technology that uses the latent heat of vaporization of the liquid medium (the latent heat is much larger than the single-phase sensible heat) to quickly remove heat.
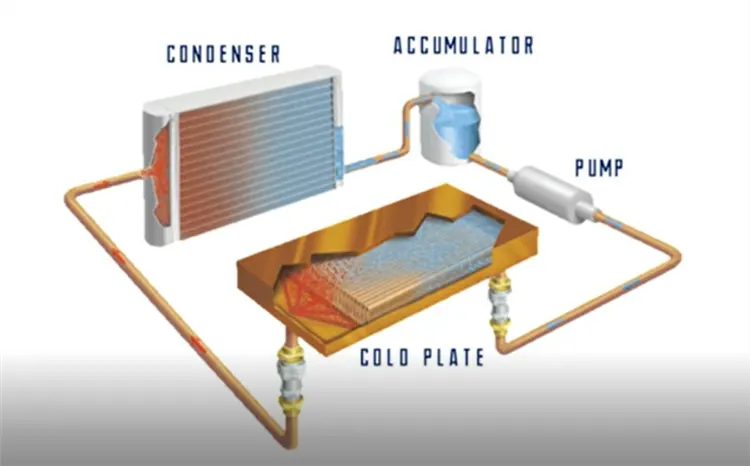
Schematic diagram of ACT's pumping two-phase cooling system

The cooling medium of the pumped two-phase cooling system evaporates at the heat source, and the latent heat of evaporation quickly takes away the heat (picture source: ACT)
The above briefly introduces the non-contact liquid cooling technology. Whether it is single-phase liquid cooling or two-phase liquid cooling, cold plates and pipelines are required to form a cooling liquid circulation system. Contact liquid cooling, that is, immersion liquid cooling, in which the electronic components of the circuit board are directly immersed in the dielectric cooling liquid, is currently the most efficient cooling technology.
With the acceleration of 5G high-speed basic network construction, the cooling demand trend of 5G base stations, cloud computing, edge computing and other data centers is increasing, and efficient and fast cooling, reducing volume and weight, convenient deployment, and reducing operation and maintenance costs are the industry's concern for heat dissipation solutions. Focus.